Note
Click here to download the full example code
Plot the decision surface of a pruneable tree using REP¶
Plot the decision surface of a pruneabletree.prune.PruneableDecisionTreeClassifier trained on pairs
of features of the iris dataset.
For each pair of iris features, the decision tree learns decision boundaries made of combinations of simple thresholding rules inferred from the training samples.
In this example, the tree is pruned using Reduced Error Pruning (REP).
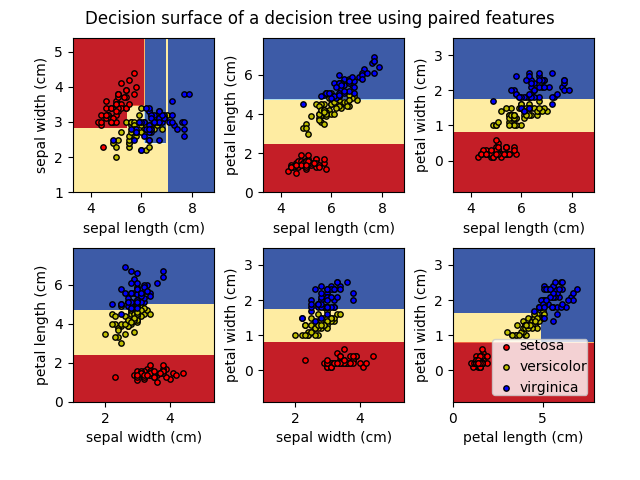
print(__doc__)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from pruneabletree import PruneableDecisionTreeClassifier
# Parameters
n_classes = 3
plot_colors = "ryb"
plot_step = 0.02
def plot_surface(iris, prune_method):
for pairidx, pair in enumerate([[0, 1], [0, 2], [0, 3],
[1, 2], [1, 3], [2, 3]]):
# We only take the two corresponding features
X = iris.data[:, pair]
y = iris.target
# Train
clf = PruneableDecisionTreeClassifier(prune=prune_method).fit(X, y)
# Plot the decision boundary
plt.subplot(2, 3, pairidx + 1)
x_min, x_max = X[:, 0].min() - 1, X[:, 0].max() + 1
y_min, y_max = X[:, 1].min() - 1, X[:, 1].max() + 1
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, plot_step),
np.arange(y_min, y_max, plot_step))
plt.tight_layout(h_pad=0.5, w_pad=0.5, pad=2.5)
Z = clf.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
plt.contourf(xx, yy, Z, cmap=plt.cm.RdYlBu)
plt.xlabel(iris.feature_names[pair[0]])
plt.ylabel(iris.feature_names[pair[1]])
# Plot the training points
for i, color in zip(range(n_classes), plot_colors):
idx = np.where(y == i)
plt.scatter(X[idx, 0], X[idx, 1], c=color, label=iris.target_names[i],
cmap=plt.cm.RdYlBu, edgecolor='black', s=15)
plt.suptitle("Decision surface of a decision tree using paired features")
plt.legend(loc='lower right', borderpad=0, handletextpad=0)
plt.axis("tight")
plt.show()
# Load data
iris = load_iris()
# Create plots
plot_surface(iris, prune_method='rep')
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 1.146 seconds)